Rheumatoid Arthritis
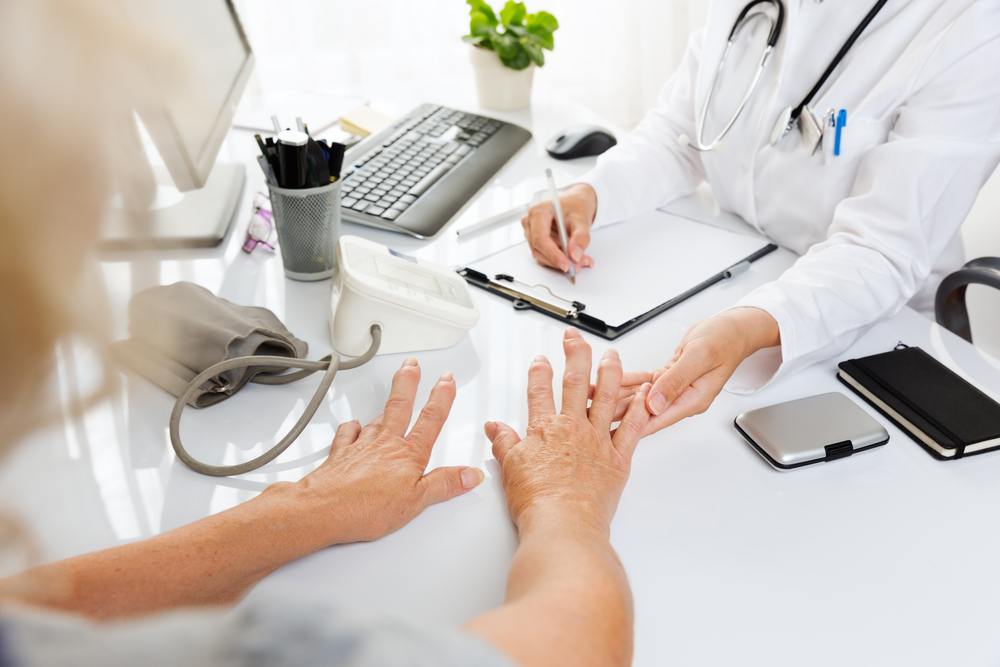
Rheumatoid arthritis is primarily an autoimmune disease that attacks the joints; the illness occurs when the immune system attacks the joint’s lining, leading to discomfort and inflammation. Additionally, the condition can affect other joints, especially the knees, wrists, and hands. Symptoms comprise stiffness of joints, especially in the morning, tenderness, swelling, joint pain, fatigue, and fever. Some treatment options are available, but this disease has no cure. In most cases, the disorder may last for years or be long-life. The condition is treated using antirheumatic drugs such as biologics that prevent joint deformity and disease advancement.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis causes patches, peeling, and swollen skin. The condition occurs due to the skin producing excess new skin cells. However, the situation is often not a severe disease but can be distressing or painful. The symptoms include itching, pain, scaly skin, and thick inflamed patches on the skin. Furthermore, imaging or lab tests are rarely required; management and treatment options include UV light therapy, topical ointments, and biologics.
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Guillain-Barre Syndrome is a type of nervous system autoimmune illness that happens when the immune system attacks healthy nerves affecting the electrical signals sent by the nerves to the brain. The condition leads to difficulty swallowing, weak muscles, vision problems, abnormal heart rates, and lack of bladder control. The syndrome is rare, and treatments help prevent further damage through high steroid doses, immunoglobulin therapy, and plasma exchange.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a type of autoimmune skin condition and chronic disease that triggers the skin to lose its pigment. Vitiligo results from the immune system attacking the melanocyte, preventing melanin production. The symptoms include grey or white hair on the eyelashes or scalp, mouth discoloration, and light or white patches of the skin on the face, arms, or feet. The recommended treatment plan includes ultraviolet (UV) light therapy, known as ultraviolet (UV) phototherapy.
Celiac Sprue
The disease attacks the digestive system. A person’s immunity reacts to gluten, a protein that foods like barley, pasta, and bread contain. Over time, the disorder may prevent the absorption of nutrients. Symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, constipation, abdominal pain, and bloating. Individuals with this disorder are advised to undergo imaging or lab tests regularly. The recommended treatment plan is the avoidance of gluten in the diet.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a type of autoimmune disease that affects the skin. The condition causes an uneven development of connective tissue in the blood vessels and skin, leading to thick and problematic skin. The state is mild in some people but, at the same time, can affect internal organs and can cause death. Research indicates the condition may be genetic, environmental, or exposure to certain drugs or viruses. The autoimmune disease mainly affects women between the ages of 30 and 50; symptoms include tightening and thickness of the skin, ulcers on the fingertips, and calcium deposits in the connective tissue. Treatment and management methods include immunosuppressants and bowel and heartburn discomfort.
Hemolytic Anemia
Hemolytic anemia is an autoimmune disease that affects the blood. The condition occurs when the immune system destroys the red blood cells. As a result, it causes an oxygen deficiency that leads to headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Treatment and management programs include corticosteroids that reduce inflammation and surgical spleen removal.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
The condition is an autoimmune illness of the digestive system; it causes chronic swelling of the digestive system giving rise to irritation and pain. The primary methods of IBD are ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. The symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, weight loss, fatigue, and rectal bleeding. Treatment methods include changing eating habits and medications such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis is a nervous system condition where the immune system mistakenly affects the myelin sheath shielding the nerves. As a result, the disease affects the transmission of signals to and fro the connected parts such as the spinal cord, nerves, and brain. Symptoms include weakness in extremities, tremors, speaking, walking, and numbness in the hands, arms, and feet. Notably, the disease does not have definite drugs for treatment; although certain medications may control and lower the symptoms, cases are different.
Type 1 Diabetes
The condition is a disease that affects hormones. The immune system attacks cells that make insulin which controls blood sugar levels. Lack of adequate insulin causes a person’s blood glucose level to rise very high, causing thirst, hunger, and fatigue. The condition is managed and controlled by administering daily insulin, regular physical activity, and diet monitoring.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
The disease is a condition that affects the glands whereby the immune system affects the thyroid glands, leading to less thyroid hormone production. Symptoms are hair loss, fatigue, muscle pain, stiff joints, constipation, and weight gain. A daily dose of levothyroxine helps raise thyroid hormone levels.
Graves’ Disease
The condition is an autoimmune disease that affects hormones. It causes the thyroid gland to become overactive and generate excess hormones, causing symptoms such as irritability, shaky hands, racing heartbeat, muscle weakness, insomnia, and weight loss. Several treatments and management options include Antithyroid medication to lower thyroid hormones level and radioactive iodine. In addition, thyroidectomy may be recommended by healthcare professionals.
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
The condition is an autoimmune disease affecting women, and antibodies attack the blood platelets necessary for blood clots. Signs include a heavy menstrual cycle, easy bruising, bleeding in the mouth and nose, abdominal pain, and red or tiny purple dots on the skin. Treatments include steroids such as oral corticosteroids; however, if corticosteroids fail to help, immune globulin injections are offered to patients.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
The condition is an illness that affects the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, and brain. Moreover, the state produces rashes in the organs. Common symptoms include rashes, fatigue, and joint pain. The condition may be treated and managed by administering antimalarial and corticosteroids.
Autoimmune Vasculitis
The condition affects the blood vessels. Generally, autoimmune vasculitis arises when the immune system attacks the blood vessels causing an inflammation that narrows the veins and arteries, allowing less blood flow. The symptoms include headache, fever, and fatigue. The treatment and management options include administering corticosteroid drugs to control the inflammation.
Addison’s Disease
This disease affects the adrenal glands producing aldosterone, cortisol, and androgen hormones. Little cortisol may affect how the body uses and stores sugar and carbohydrates. Aldosterone deficiency may lead to excess potassium and sodium loss in the bloodstream. The symptoms include low blood sugar, weight loss, and weakness. Treatment plans include hormone replacement therapy and oral corticosteroids to correct the level of steroids.
Sjögren’s Syndrome
The condition is an autoimmune disease that attacks the glands that lubricate the mouth and eyes. The primary symptoms include dry mouth and eyes but may also affect the skin or joints. The treatment method comprises administering hydroxyl chloroquine and methotrexate, which suppress the immune system.
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
The disease affects both genders but mainly affects women. The immune system destroys the bile duct leading to a buildup of bile in the liver that causes pain. The damage hardens the liver and ultimately stops functioning. Symptoms include dry mouth and eyes, yellowing, itchy skin, and fatigue. Nevertheless, the condition has no cure, but medications such as Ursodeoxycholic acid slow the disease process and prevent further complications.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia Areata mainly affects women; the immune system affects hair follicles. The condition is not health-threatening though it affects an individual’s appearance. An individual can recover from the disease since it is temporary. The hair loss is quick, and the follicles can grow. The main symptom is patchy hair loss on the face, scalp, and other body parts. Applying corticosteroids on the bald spots and minoxidil to help maintain hair growth. Moreover, some people treat the condition using natural methods, and research supports natural products in alopecia disease.
Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease that destroys the nerves. The condition deteriorates after periods of movement and improves after rest. The antibodies bind to the nerves, which cannot stimulate muscles properly. Additionally, the disease is common in men above sixty years and women below forty years. The main symptoms of the condition are droopy eyelids, double vision, and difficulty swallowing. This health condition has no cure. However, pyridostigmine remains the best treatment option.